DumagueteInfo has a new home and you are viewing an archived article. Get the latest of what the new DumagueteInfo has to offer after reading this article. Thank you!
Read more →
Philippine Government Administrative Divisions and Its Purposes
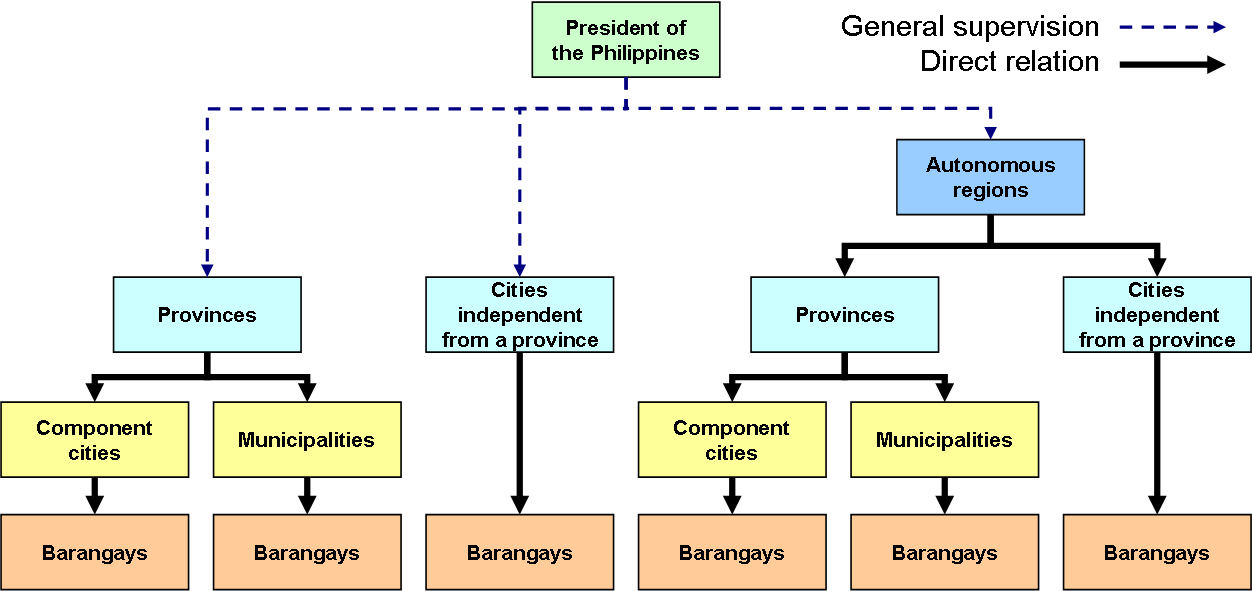
The Philippines is composed of different government administrative divisions aside from its 3 equally supreme branches known as the Executive Branch, Legislative Branch and the Judiciary Branch. The Philippine Administrative divisions are commonly known as the Local Government Units (LGU). The Local Government Units are further categorized into Autonomous Region, Provinces, Municipalities or Cities and Barangays. The president only exercises General Supervision on the Administrative divisions. The local government units can only enjoy local autonomy. It aids the government in carrying out its purpose and functions so Administrative Divisions only have authority limited to Administrative functions like collection of taxes, implementing policies and the like but there are always exceptions to this rule just like provinces having their own legislative bodies.
Government Administrative Division Levels
Autonomous Region
- Autonomous Region of Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) is the only autonomous region here in the Philippines. This region is given a special privilege of having additional power. They technically have higher powers than the other LGUs.
Provinces
- Apart from the special Autonomous Region, Provinces have the highest level of political power among the administrative divisions of the Philippines. However, provinces also form part of the regular regions of the Philippines. Provinces are headed by Governors and they have their own legislative department known as the Sangguniang Panlalawigan. The province’s legislature is responsible for making Ordinances and Resolutions for the benefit of their respective provinces. Its powers and duties are governed by the Local Government Code of 1991.
- The Sangguniang Panlalawigan is responsible for maintaining peace and order in the whole province as well as reviewing the city ordinances passed by the Sangguniang Panlungsod.
- They also have the power to impose fines on violators of provincial ordinances and other fines deemed necessary to promote common good and peace and order in the community.
Cities & Municipalities
- Provinces are composed of the different towns and cities within them. A city is headed by the City Mayor and his subordinates. The city is considered a corporate entity so it has the power to purchase, take, receive, acquire and dispose assets for the benefit of the public. They are even entitled to the power of Eminent Domain where they can seize a private property for public use.
- Cities having a population of at least 250,000 are entitled to have one representative in the Congress or the House of Representatives.
- Cities are also categorized into three types and they are as follows: Highly Urbanized Cities, Independent Component Cities and Component Cities. A city can only be classified as highly urbanized if its population exceeds 200,000 residents as verified by the National Statistics office and should have its latest yearly income of P500,000,000.00. As for Independent Cities, it must have at least 150,000 residents and an annual income of at least P350,000,000.00. Cities not having these qualifications are considered component cities.
Barangay
- This is the smallest Local Government Unit in the Philippines. It is headed by a Barangay Captain together with Barangay Councilors. Their function is to promote peace and order in a smaller scope. They are entitled to have their own risk reduction team that will cater to the needs of their residents.
- They assist the City Officials in implementing ordinances and resolutions. Barangays have a great role in the successful implementation of ordinances because it is relatively small in scope thus it can be more controllable than that of the higher levels of LGUs.